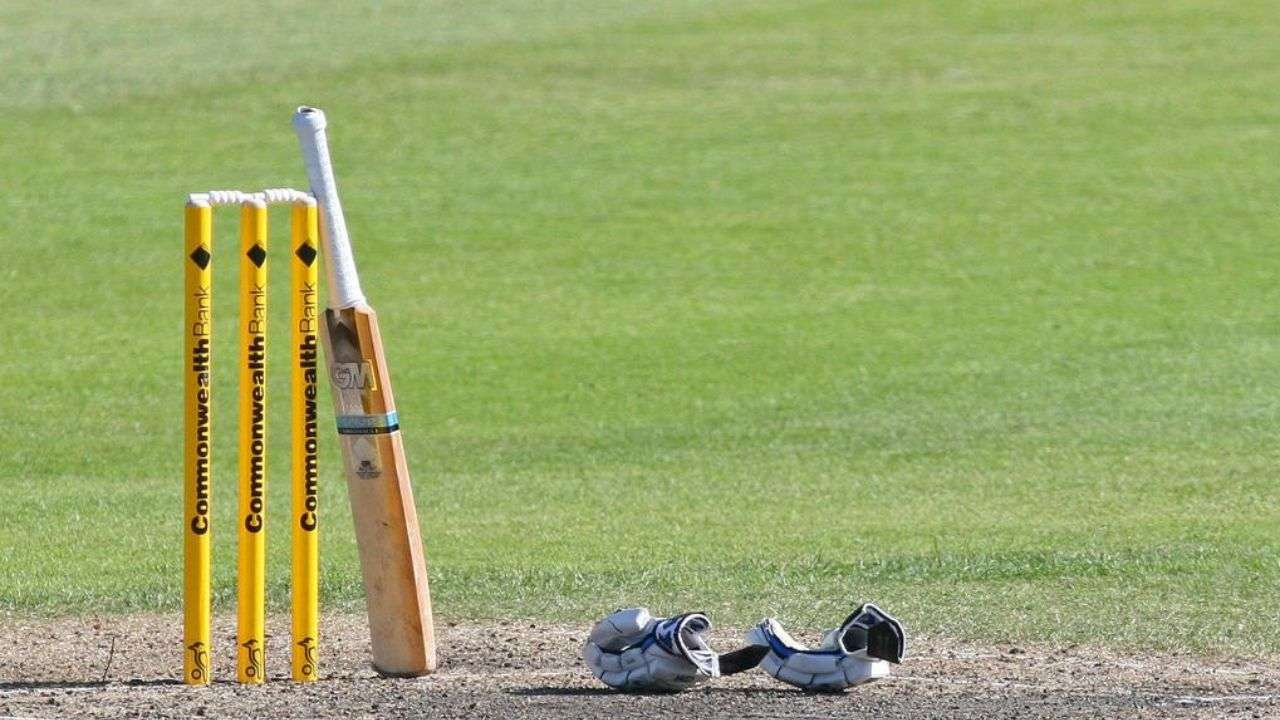

Overview
played between two teams of 11 players.
Australia is the current world champion (2015). Countries like India, Pakistan, England, South Africa, New Zealand, West Indies and Sri Lanka are equally prominent cricket teams.
Objectiv
Is played out on the cricket field. The purpose of the game is that one team should make more runs than the rival team. This is all about the effort to make more runs, while limiting the score and eliminating the opposition team's batsmen. Further in the document, any game can understand its popular rules and rules closely.
- LBW - Leg Before Wicket - According to the LBW rule, the batsman should not use the body in place of his bat to prevent the ball from being hit by the wicket.
- Silly Point - Seal Pointe is very close to the batsman
- Ashes - Ashes is a Test cricket series between England and Australia
- Maiden over - An over where the batsman can not make any runs
- Out Swing - After the fall, the ball that goes away from the batsman is called out of the swing
- Pitch - Pitch is 22 yards, stumps on either side
- Follow-On - The score created by a team is 200 runs short by the score made by the other team, the follow-on rule applies
- Drive - The task of killing the ball while batting is called a shot or stroke or drive
- Chainaman - A good performing speaker or a batsman is called chaiamanain
- Bye - Sometimes the ball gets out without touching the bat or body of the batsman. If runs on it, then it is considered to be a run
- Stamp - On each side of the pitch, a group of three wooden stumps and two chicks are called vicket.
- No-ball - Fiddling forward ahead of a given line by the bowler is called no ball
- Hattrick - It takes a wicket on three consecutive balls or a six or four
- Run Out - The batsman can not reach the wicket in the event of a run and if the ball is on the wicket, the batsman is run out.
- Swing - If the ball tally inserted by the speaker is eaten outside or inside the house then it is called swing inside or outside.
- Bowler - The ball is the bowler who bowls the ball
- Batsman - Batsman is the only player to hit the ball on the pitch by the bowler
- Wide - The ball is wide open from the ball stumps inserted on the pitch by the bowler
- Throw - throwing a ball by any fielder or player is thrown
- Covers - between the slip and the point I called a player who is covered
- Slip - The player slips in the shape of the wicket keeper
- Hook - The shot ball killed by the batsman is hooked
Popular Terms in cricket
- Striker - The batsman facing the bowler is a collar striker and the opposite end is called a non-striker.
- Off-side / leg-side - A half ground is called off-side and the other side is called leg-side. From the point of view of right-handed batsmen, the pitch in front of your body, ie the right side of the pitch, is called off-side when you take the strike. Similarly, while taking the stripe of the left half of the pitch, the back pitch of his body is called leg side.
- Run - This is the basic unit of scoring in cricket. This happens when a strike batter hits the ball and runs along the non-striker between the stump. It is usually made in people, twins and threes.
- Four - The ball hit by the batsman crosses the boundary by rolling it on the ground. Again, it is called a boundary or four runs.
- Six - A shot that ensures the ground of the ball directly outside the rope is called six or six runs, the batsman is allocated.
- No-ball - If a bowler's feet crosses the popping crease while delivering the ball, then it is called no-ball. The ball which is directed at the back of the batsman without standing on the ground is also no-ball.
- Wide - A ball that is thrown away from the batsman and turns wide on the off side of the batting end, it is called wide. In another definition, the ball is thrown away, which is bounce over the head of the batsman after pitching, which is also called wide.
- Out - When a batsman gets out, he gives the opportunity to play the next person in the batting side until 10 out of 11 players are out in different ways. The most common methods of bowling, catch, run-out, LBW and stumped are
- Bold - It's a way to get out, where the batsman misses the ball, and the stump stops behind.
- Captured - a batsman is declared out when the fielder catches the ball completely which is hit by the batsman. If it is caught by the wicket keeper, then it is called a catch-back.
- LBW - LBW means leg-before wicket. A batsman is declared as lbw when he tries to play the ball with the body, which is directed at the stump.
- Run-out - If a fielder troubles the stump with a ball in hand, while the batsman is not in the crease after playing the shot, then the batsman is declared a run-out.
- Stumped - A batsman goes out of the crease to play a ball and misses, the keeper collects the ball and kills the stump with the ball in his hand. Then, the batsman is declared a stump out.
- Spin bowling - Bowlers run a short distance from the stumps and leave the ball using the wrist or fingers to achieve maximum revolutions. The ball jumped into the air after pitching. Off break and leg break spin are two varieties of bowling.
- Fast bowling - The bowlers bounce and deliver the ball to the batsman at a high speed. To do this, they take long run-ups from the stumps. Slow-medium, medium-fast, and fastest fast fast bowling varieties.
- Extra Run - All runs given by the fielding team where the batsman does not hit the ball with the bat, is considered to be an extra run. For example, wide, no-ball, etc.
- Inings - A session of batting and bowling where either the batting team is all-out or the allowed number of overs to be bowled by the fielding team is completed.
Cricket - Equipment
Since cricket is a ball and ball game, players have to wear protective gear to prevent injury. In this lesson, we will discuss about all the important gears and instruments that the players use when playing the game.
- Bats - Bat is a well-carved tool made of special wood, which has a handle to hold and play. These vary in weight and size with the age and necessity of the batsman.
- Ball - It is a circular object that is made of cork and covered with leather. Two pieces of leather are attached around the cork ball. Ball color for test matches is red and white for ODI and T20 matches.
- Keeper gloves - These fingers of both hands are worn to protect from injuries. The clothes and leather are stitched together in the shape of fingers and palm to fit together. There are finger gaps with cork tips for more protection in the inside of the glove.
- Batsman glove - This gear is the same in size but compared to the keeper gloves is smaller and soft on the outside. It is used to hold the ball firmly. In the finger part of the glove, there is extra protection with hard sponge on the outer area.
- Keeper / batter pad - These are worn for the safety of lower body parts of the batsman / guard. They are made from cloth and leather. The front part of the pad is very hard because there is a plastic or wood link below. The back section is spongy and soft so that they can sleep comfortably. Keeper pads are slightly less than the pads of the batsmen.
- Helmets - A head gear for the batsman / keeper while batting or wicket-keeping behind the stump. It is a mixture of metal and hard plastic. There is a metal grill on the front for face protection.
- Stumps - They are cylindrical and are long in size, like the ends with the spear. This end goes into the ground so that the stump starts standing in the ground.
- Bells - The smallest equipment to be installed on the Bell Stumps. It helps the easy decision by the umpires to dismiss the batsman when the wicket breaks.
Cricket - Formats
In the Golden Age, cricket was played for days because each team played more than 100 overs in almost a day. We can relate to the current format of Test Cricket. In the early days of cricket, there were eight legal deliveries in one over. Gradually, new formats and rules came into existence and reduced to six legal deliveries in all over one formats. In this chapter we are going to discuss various formats of professional cricket and some rules about them.
Test cricket
Test cricket is considered to be the highest level format because it requires both mental and physical strength to excel. All players wear white tees and trousers for this format. Red cricket ball is used to play. The initial format of Test cricket was played for six days with reserve one day as reserve. Area restrictions are quite different compared to limited over cricket.
If necessary, teams A and B have to play two innings. 90 o'clock is to be thrown every day. Team A had earlier scored an X while batting. If Team A declares its innings or is all out, then Team B goes for batting. Team B must have X or more runs to make a good chance to win the match. Then, Team A goes to bat another time and sets goals for Team B. Now Team B has to achieve the target in the remaining time and bowl in the overs.
If Team B is all-out during the chase in the second innings, Team A is declared the winner, otherwise the match draws between the teams.
One-day international
There is a limited over format of one-day international cricket. It was introduced in the 1980s and more than 60 sides were bowling. Dress code was similar to Test cricket. Over the years, this format went through a lot of changes in the rules and it was reduced to 50 in one side and colorful uniform. The red ball was replaced with a white ball.
The batting of Team A was to set a goal for Team B in the first 50 overs. Batting at number two, Team B had to chase down the target in the same over. If they fail to do so, Team A is declared the winner of team A despite Team B or not.
T20 International
T20 is the latest and most successful format of cricket. It attracted the audience very much on the field and saw the match. Cricket became a widespread sport in this format and new countries such as USA, Malaysia, Canada and Netherlands quickly adapted it. It originated in the Caribbean islands, West Indies. Each team gets to play 20 overs. Since it is the smallest format of the game, it is played under the flood light.
While batting first, Team A set a goal for Team B in 20 overs. Team B is aiming at the second place with fixed overs.
Team B is declared the winner if they achieve the goal, then Team A is declared victorious. Team A is still declared the winner, when they stop Team B from limiting the number of runs required and do not take them out of bowling.
Cricket - Playing Environment
Cricket is a team game and played on a large field. Pitch is prepared for any format of the match in the center and field. Later, stumps are placed along the width of the pitch and the players are called on the field to start the game. The fielding team will have 11 players who will defend the boundary and two opposition batsmen will come to bat. There will be two umpires on the field to monitor the proceedings of the match.
Cricket Field Dimensions
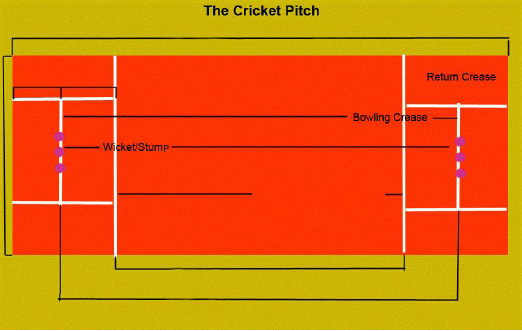
The game is played on a spherical flat ground, possibly with a pitch in the form of a center. The length of the pitch is 24-yards and the width is 4-yards. A rope is kept around the ground at 80 yards from the pitch. This rope is celebrated as boundary. Stumps are rooted in between 22-yards between both ends. Two carved small pieces of wood are placed on the stumps, which are called bell. White parallel lines are drawn on both ends of the stump, called the batting / bowling crease. It is 1.2 meters from the stumps. Another set of parallel lines is drawn vertically for the batting crease, which is called the return crease. It is half a meter away from the length of the pitch.
Dimensions of Cricket Equipment
ICC has made some rules for cricket equipment with the rules of the game. The bat, ball, glove, pad and all other equipment have to meet the standards set by the governing body. It is used not only on the size of the equipment, but also on devices which should be consistent with the standards set by the ICC. There is a list of cricket equipment with the permission given below -
-
Bat − A cricket bat should not be more than 38 inches in length and 4.25 inches wide.
-
Ball − The cricket ball must weigh between 155.9 and 163 g. Apart from weight, the circumference should be between 224 and 229 mm.
-
Keeper glove − The keeper glove doesn’t have specific measurement but should not be made of stretchable material. The glove has webbing between thumb and the index finger.
All other tools are used to protect body parts, so there are no specific measures or design standards with security, as a priority.
Tag: Cricket - Equipment, Cricket - Formats, Cricket - Playing Environment, Dimensions of Cricket Equipment, Some Important Terms Related to cricket, Cricket Se Sambandhit Mahatvapurn Shabdavali, Important vocabulary related to cricket
 Dear Reader, My name is Manisha Dubey Jha. I have been blogging for 3 years and through the Fast Read.in I have been giving important educational content as far as possible to the reader. Hope you like everyone, please share your classmate too. As a literature person, I am very passionate about reading and participating in my thoughts on paper. So what is better than adopting writing as a profession? With over three years of experience in the given area, I am making an online reputation for my clients. If any mistakes or wrong in the article, please suggest us @ [email protected]
Dear Reader, My name is Manisha Dubey Jha. I have been blogging for 3 years and through the Fast Read.in I have been giving important educational content as far as possible to the reader. Hope you like everyone, please share your classmate too. As a literature person, I am very passionate about reading and participating in my thoughts on paper. So what is better than adopting writing as a profession? With over three years of experience in the given area, I am making an online reputation for my clients. If any mistakes or wrong in the article, please suggest us @ [email protected]
Read More.
