Notifications
A notification is a message that you can display to the user outside the normal UI of your application. When you tell the system to issue a notification, it appears as an icon in the first notification area. To see the details of the notification, the user opens the notification drawer. Both notification areas and Notification Drawer are system-controlled areas that users can view at any time.
The Android Toast class provides an easy way for users to show an alert, but the problem is that these alerts are not consistent, which means that the warning flash for a few seconds on the screen and then disappears.
In order to see the details of the notification, you will have to select the icon that will detail the notification drawer. When working with the virtual device with the emulator, click and drag the status bar to expand it, which will give you details as follows. It will only be 64 DP long and will be called normal view.
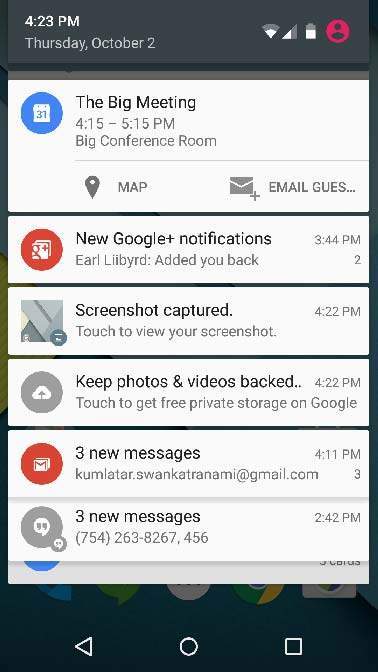
Above expanded form can have a Big View which will have additional detail about the notification. You can add upto six additional lines in the notification. The following screen shot shows such notification.
Create and Send Notifications
You have simple way to create a notification. Follow the following steps in your application to create a notification −
Step 1 - Create Notification Builder
As a first step is to create a notification builder using NotificationCompat.Builder.build(). You will use Notification Builder to set various Notification properties like its small and large icons, title, priority etc.
NotificationCompat.Builder mBuilder = new NotificationCompat.Builder(this)Step 2 - Setting Notification Properties
Once you have Builder object, you can set its Notification properties using Builder object as per your requirement. But this is mandatory to set at least following −
-
A small icon, set by setSmallIcon()
-
A title, set by setContentTitle()
-
Detail text, set by setContentText()
mBuilder.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.notification_icon);
mBuilder.setContentTitle("Notification Alert, Click Me!");
mBuilder.setContentText("Hi, This is Android Notification Detail!");You have plenty of optional properties which you can set for your notification. To learn more about them, see the reference documentation for NotificationCompat.Builder.
Step 3 - Attach Actions
This is an optional part and if you want to attach an action to the alert then it is necessary that an action allows users to go from the information directly to an activity in your application, where they can see one or more events or further Can work.
The action is defined by a pending intentant in which an activity begins in your application. With a hint to delay the project, call the appropriate method of NotificationCompat.Builder. For example, if you want to start the activity, the user clicks the notification text in the notification drawer, then you can add a pending identity by calling setContentIntent ().
A pending element object helps you take action on behalf of your application, often later, regardless of whether your application is running or not.
We take the help of stack builder objects, which will include an artificial back stack for initial activity. This ensures that navigating backward by activity leaves your app on the home screen
Intent resultIntent = new Intent(this, ResultActivity.class);
TaskStackBuilder stackBuilder = TaskStackBuilder.create(this);
stackBuilder.addParentStack(ResultActivity.class);
// Adds the Intent that starts the Activity to the top of the stack
stackBuilder.addNextIntent(resultIntent);
PendingIntent resultPendingIntent = stackBuilder.getPendingIntent(0,PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
mBuilder.setContentIntent(resultPendingIntent);
Step 4 - Issue the notification
Finally, you pass the Notification object to the system by calling NotificationManager.notify() to send your notification. Make sure you call NotificationCompat.Builder.build() method on builder object before notifying it. This method combines all of the options that have been set and return a new Notification object.
NotificationManager mNotificationManager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
// notificationID allows you to update the notification later on.
mNotificationManager.notify(notificationID, mBuilder.build());The NotificationCompat.Builder Class
The NotificationCompat.Builder class allows easier control over all the flags, as well as help constructing the typical notification layouts. Following are few important and most frequently used methods available as a part of NotificationCompat.Builder class.
| Sr.No. | Constants & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Notification build()
Combine all of the options that have been set and return a new Notification object. |
| 2 | NotificationCompat.Builder setAutoCancel (boolean autoCancel)
Setting this flag will make it so the notification is automatically canceled when the user clicks it in the panel. |
| 3 | NotificationCompat.Builder setContent (RemoteViews views)
Supply a custom RemoteViews to use instead of the standard one. |
| 4 | NotificationCompat.Builder setContentInfo (CharSequence info)
Set the large text at the right-hand side of the notification. |
| 5 | NotificationCompat.Builder setContentIntent (PendingIntent intent)
Supply a PendingIntent to send when the notification is clicked. |
| 6 | NotificationCompat.Builder setContentText (CharSequence text)
Set the text (second row) of the notification, in a standard notification. |
| 7 | NotificationCompat.Builder setContentTitle (CharSequence title)
Set the text (first row) of the notification, in a standard notification. |
| 8 | NotificationCompat.Builder setDefaults (int defaults)
Set the default notification options that will be used. |
| 9 | NotificationCompat.Builder setLargeIcon (Bitmap icon)
Set the large icon that is shown in the ticker and notification. |
| 10 | NotificationCompat.Builder setNumber (int number)
Set the large number at the right-hand side of the notification. |
| 11 | NotificationCompat.Builder setOngoing (boolean ongoing)
Set whether this is an ongoing notification. |
| 12 | NotificationCompat.Builder setSmallIcon (int icon)
Set the small icon to use in the notification layouts. |
| 13 | NotificationCompat.Builder setStyle (NotificationCompat.Style style)
Add a rich notification style to be applied at build time. |
| 14 | NotificationCompat.Builder setTicker (CharSequence tickerText)
Set the text that is displayed in the status bar when the notification first arrives. |
| 15 | NotificationCompat.Builder setVibrate (long[] pattern)
Set the vibration pattern to use. |
| 16 | NotificationCompat.Builder setWhen (long when)
Set the time that the event occurred. Notifications in the panel are sorted by this time. |
Example
Following example shows the functionality of a Android notification using a NotificationCompat.Builder Class which has been introduced in Android 4.1.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | You will use Android studio IDE to create an Android application and name it as fastread under a package com.example.notificationdemo. While creating this project, make sure you Target SDK and Compile With at the latest version of Android SDK to use higher levels of APIs. |
| 2 | Modify src/MainActivity.java file and add the code to notify(""), if user click on the button,it will call android notification service. |
| 3 | Create a new Java file src/NotificationView.java, which will be used to display new layout as a part of new activity which will be started when user will click any of the notifications |
| 4 | Modify layout XML file res/layout/activity_main.xml to add Notification button in relative layout. |
| 5 | Create a new layout XML file res/layout/notification.xml. This will be used as layout file for new activity which will start when user will click any of the notifications. |
| 6 | No need to change default string constants. Android studio takes care of default string constants |
| 7 | Run the application to launch Android emulator and verify the result of the changes done in the application. |
Following is the content of the modified main activity file src/com.example.notificationdemo/MainActivity.java. This file can include each of the fundamental lifecycle methods.
package com.example.notificationdemo;
import android.app.Notification;
import android.app.NotificationManager;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.support.v7.app.ActionBarActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity {
Button b1;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
b1=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button);
b1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Notify("You've received new message");
}
});
}
private void Notify(String notificationTitle, String notificationMessage){
NotificationManager notificationManager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
Notification notification = new Notification(R.drawable.abc,"New Message", System.currentTimeMillis());
Intent notificationIntent = new Intent(this,NotificationView.class);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0,notificationIntent, 0);
notification.setLatestEventInfo(MainActivity.this, notificationTitle,notificationMessage, pendingIntent);
notificationManager.notify(9999, notification);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
// Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will
// automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long
// as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml.
int id = item.getItemId();
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
if (id == R.id.action_settings) {
return true;
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}Following will be the content of res/layout/notification.xml file:
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="400dp"
android:text="Hi, Your Detailed notification view goes here...." />
Following is the content of the modified main activity file src/com.example.notificationdemo/NotificationView.java.
package com.example.notificationdemo;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
public class NotificationView extends Activity{
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.notification);
}
}Following will be the content of res/layout/activity_main.xml file −
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context="MainActivity">
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Notification Example"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:textSize="30dp" />
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Tutorials point "
android:textColor="#ff87ff09"
android:textSize="30dp"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="48dp" />
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/imageButton"
android:src="@drawable/abc"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="42dp" />
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Notification"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_marginTop="62dp"
android:layout_below="@+id/imageButton"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
Following will be the content of res/values/strings.xml to define two new constants −
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
name="action_settings">Settings
name="app_name">fastread
Following is the default content of AndroidManifest.xml −
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.notificationdemo"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
android:name="com.example.notificationdemo.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
android:name=".NotificationView"
android:label="Details of notification"
android:parentActivityName=".MainActivity">
android:name="android.support.PARENT_ACTIVITY"
android:value=".MainActivity"/>
Try to run your Fastread application. I believe that you had made your AVD while setting up the environment. To run an app from Android Studio, open one activity file from your project and click the Run icon from the toolbar. Android Studio installs the app on your AVD and starts it and if everything is ok with your setup and application, it will be displayed
Now click on the button, in the top message "New Message Alert!" Will appear on the screen in a moment, and after that you will run on the screen with a small icon in the top left corner.
Now lets extend the view, long click on the small icon, after one second it will display date information and this happens when you drag and drag the status bar without releasing the mouse. You will see the status bar and you will get a screen
Big View Notification
The following code snippet demonstrates how to alter the notification created in the previous snippet to use the Inbox big view style. I'm going to update displayNotification() modification method to show this functionality −
protected void displayNotification() {
Log.i("Start", "notification");
/* Invoking the default notification service */
NotificationCompat.Builder mBuilder = new NotificationCompat.Builder(this);
mBuilder.setContentTitle("New Message");
mBuilder.setContentText("You've received new message.");
mBuilder.setTicker("New Message Alert!");
mBuilder.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.woman);
/* Increase notification number every time a new notification arrives */
mBuilder.setNumber(++numMessages);
/* Add Big View Specific Configuration */
NotificationCompat.InboxStyle inboxStyle = new NotificationCompat.InboxStyle();
String[] events = new String[6];
events[0] = new String("This is first line....");
events[1] = new String("This is second line...");
events[2] = new String("This is third line...");
events[3] = new String("This is 4th line...");
events[4] = new String("This is 5th line...");
events[5] = new String("This is 6th line...");
// Sets a title for the Inbox style big view
inboxStyle.setBigContentTitle("Big Title Details:");
// Moves events into the big view
for (int i=0; i < events.length; i++) {
inboxStyle.addLine(events[i]);
}
mBuilder.setStyle(inboxStyle);
/* Creates an explicit intent for an Activity in your app */
Intent resultIntent = new Intent(this, NotificationView.class);
TaskStackBuilder stackBuilder = TaskStackBuilder.create(this);
stackBuilder.addParentStack(NotificationView.class);
/* Adds the Intent that starts the Activity to the top of the stack */
stackBuilder.addNextIntent(resultIntent);
PendingIntent resultPendingIntent =stackBuilder.getPendingIntent(0,PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
mBuilder.setContentIntent(resultPendingIntent);
mNotificationManager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
/* notificationID allows you to update the notification later on. */
mNotificationManager.notify(notificationID, mBuilder.build());
}Now if you will try to run your application then you will find following result in expanded form view.
